|
Music Genie: Interactive, Content-Based Browsing of Music Based on Thumbnail Playback
Problem statement
More people enjoy music from high-capacity portable
players and from internet music services. Developing
natural methods for exploring the growing music
collections is now a critical need. In this work we
developed a prototype system for interactive,
computer-assisted music browsing based on the direct
presentation of short music thumbnails.
Outline
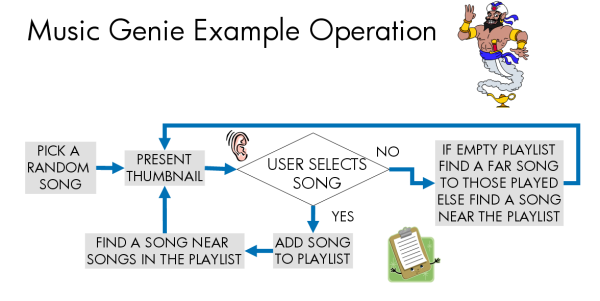
Music Genie refers to audio
processing technologies for quick and easy music browsing and
discovery. We built research prototype software that allows users to
quickly generate playlists from a collection of thousands of songs.
Our software provides an interactive, content-adaptive,
thumbnail-based presentation of music. The software accepts user
inputs interactively during use, and it consecutively presents short
music thumbnails for quick browsing. This direct, interactive
presentation of music makes our system simple and transparent for
users. Unobstrusively, the user's interactions (or lack thereof) are
input into a real time system that, based on the prior analysis of
the music content, adaptively presents a potentially interesting new
song thumbnail. This technology may be used to 1) assist users
discover music for purchase from a web music store; 2) allow users
to browse their PC music collection based on current taste; and 3)
allow intelligent browsing, playback or playlist generation in
small, interface-limited, music players.
 A white paper describing the technology is found
here.
A white paper describing the technology is found
here.
Last Modified:
Monday, July 23, 2007 11:01:40 -0700
Reducing Audio Noise Using Spectrogram Random Textures
Problem statementMany are unpleasantly
surprised by the unexpected noise and the low quality of the audio
of their home video clips. The goal here is to improve the quality
of consumer generated audio: audio captured using consumer
electronics devices under uncontrolled conditions. Making the
problem harder, consumer-generated audio is not speech alone. Many
indoor audios contain music, and many outdoor audios contain
important natural sounds such as waterfalls, ocean waves, etc. In
this work, we developed techniques for enhancing consumer-generated
audio. The example described below applies to digital camera zoom
motor noise, a degradation commonly found in short video clips.
Outline
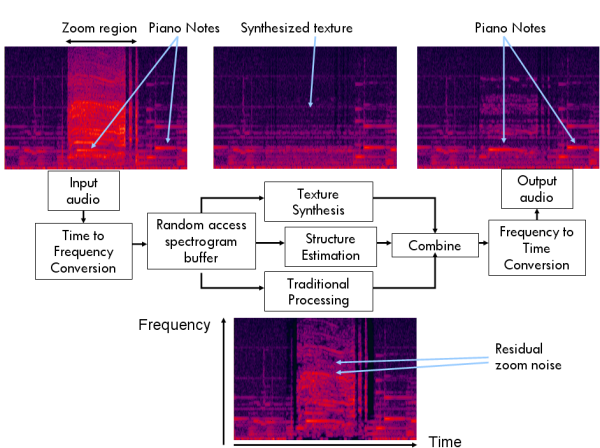
his work involves audio enhancement when a strong, additive noise
is present only during a known or easily detected period of moderate
length (of around one second). The signals may contain intelligible
components such as speech or music, and may also contain desired,
but unintelligible, background components such as rivers or
waterfalls. A first estimate synthesizes the unintelligible
components from the noise-free neighboring spectrogram. A second
estimate recovers the intelligible components using spectral
attenuation. The two estimates are combined using ideas from
statistical process control. Tests with audio containing digital
camera zoom motor noise, and with simulations, validate the
approach.
Technical details are found here.
Last Modified: Wednesday, 07/18/2007 13:55:47 -0700
|
