|
Representative (Honest) Image Thumbnails
Problem statement
Traditional (filter and subsample) image reduction does not
retain sufficient information to allow browsing and image selection
from image collections. In this work we use image analysis to
develop non-traditional resizing techniques that preserve the
information about the image quality of the underlying originals.
Outline
Image thumbnails are commonly used for selecting
images for display, sharing or printing. Current, standard
thumbnails do not distinguish between high and low quality
originals. Both sharp and blurry originals appear sharp in the
thumbnails, and both clean and noisy originals appear clean in the
thumbnails. This leads to errors and inefficiencies during image
selection. In this research, we are using image analysis to generate
thumbnails that better represent the quality of their original high
resolution images.
We first build a standard thumbnail, then estimate a
local blur using local measures from the the input image and the
standard thumbnail (which we use as a high quality reference) and
finally apply a space-varying Gaussian filter to the standard
thumbnail. To add the noise component, we extract the residual (the
noise component) from a denoiser, and subsample it, preserving the
variance of the noise found in the high resolution original.
This work is applicable to image browsing on
embedded, web-based and PC applications. These new thumbnails
provide a quick, natural way for users to identify images of good
quality, while allowing the viewer’s knowledge to select desired
subject matter.
 |
| New thumbnail |
Standard thumbnail |
| New thumbnail reflects local
blur. View original by clicking
here. |
 |
| New thumbnail |
Standard thumbnail |
| New thumbnail reflects image
noise. View original by clicking
here. |
Further details, describing an algorithm that reflects the local
blur and the noise of the originals, together with subjective
evaluation of the results is found in HP labs technical report
HPL-2007-88, found
here .
Last Modified:
Tuesday, July 24, 2007 09:11:36 -0700
PathMarker: A System for Capturing Trips
Problem statement
It is difficult to organize collections of rich
media. Memories of a trip are hard to relive and share
without context. Current automatically generated slide
shows are hard to follow because they lack location and
time context. In this research, we built prototypes that
we call PathMarker, that address these problems by
augmenting rich media with automatic capture of path
context.
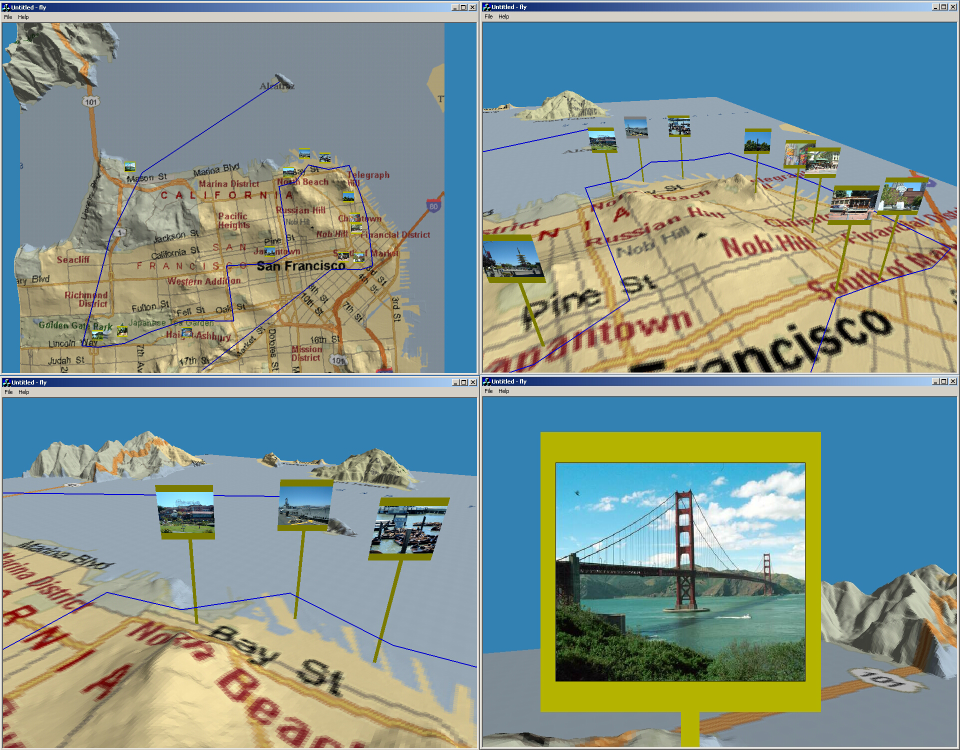 |
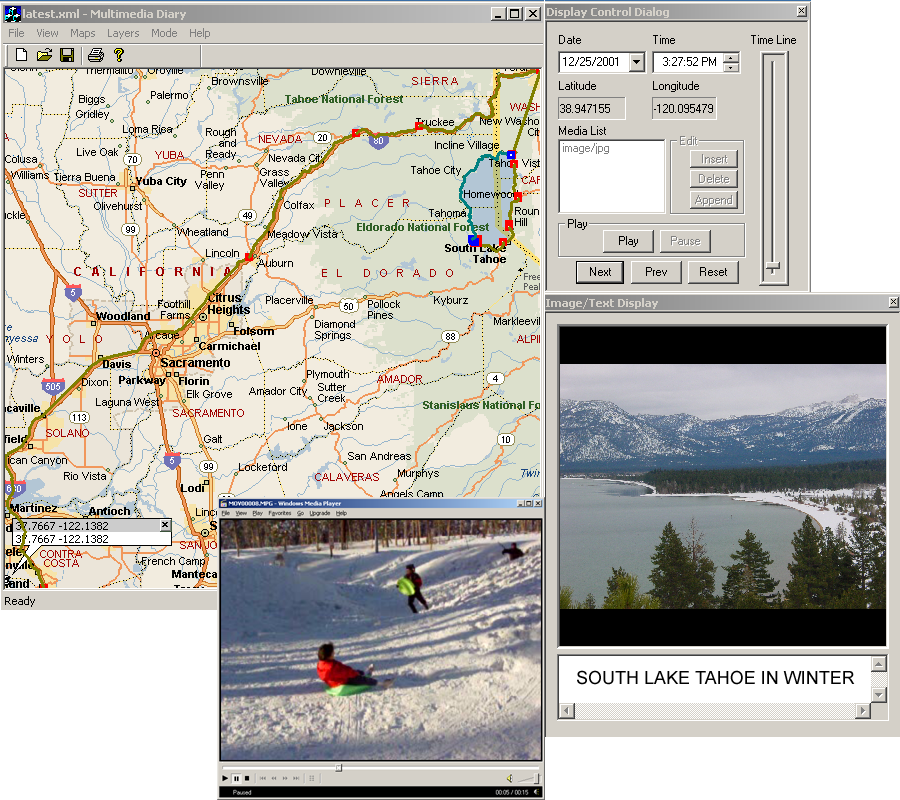 |
| Example screenshots from prototype 3D system
on the left and prototype trip player application on the
right. Click on the images above for larger versions. |
Outline
Central to capturing a trip is knowing where you were, and when
you were there. Combining continuous path data with media
(Path-Enhanced Media or PEM) offers substantial advantages over the
previous approach of tagging individual media with time and
location. Accurate paths allow for the 1) automatic creation of an
organized, rich media diary that helps people remember, enrich,
share and relive past trips and helps them to plan for new trips; 2)
embellishment of trips using third party stock media and non-media
information; 3) the natural, automatically created presentation of
trips; and 4) new kinds of media annotation, sharing, dissemination,
search and organization.
By combining GPS path information with digital media, we have
built prototype systems for gathering, editing, presenting and
browsing PEM. We developed 1) a methodology for gathering PEM with
off-the shelf hardware; 2) software for automatic conversion of the
raw path data and media into an application independent XML
representation; and 3) example PEM applications. A first application
provides map-overlaid trip editing, presentation and browsing. A
second application provides a 3D immersive environment with digital
elevation maps for automatic trip flybys and for browsing. A third
experiment involved generating an interactive DVD from path-enhanced
media, resulting in a compelling presentation of a vacation trip.
Further details are found
here
Last Modified: Wednesday, 07/18/2007 13:55:47 -0700
|
